In the quest to find some of the most effective ways of preventing dementia, experts have been pursuing an angle that is worth looking into – omega 3 and dementia.
Omega 3 remains one of the diet components that come highly recommended concerning brain health.
New reports also link the consumption of omega 3 to dementia prevention.
Read on to find out more about how omega 3 may potentially help with the prevention of dementia.
Omega 3 Fatty Acids For Dementia Treatment
What is Omega 3?

To better understand the topic of omega 3 and dementia, it is best to start with explaining what omega 3 is.
It is a type of polyunsaturated fat present in the cell membrane. It is an umbrella term for all omega 3 fatty acids. These include docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).
The human body produces omega 3 but at a very slow rate which means that you should get it from your diet. Plant-based omega 3 rich nuts, vegetables, and seeds are good sources.
Oily fish like tuna, mackerel, salmon, and herring are rich in omega 3.
Importance of Omega 3

Omega 3 plays a significant role in the brain from when the fetus is developing to old age.
Omega 3 fatty acids are vital for the structural development of the brain because they improve mood and support neurotransmitter signaling according to a nutritionist at BioCare Mana, Chouchane.
Scientists believe that the brain cells with high omega 3 levels communicate better with other cells, a move that is crucial for brain function.
When the body takes the fat, it breaks down some of it to carry out various functions. Some of these reduce the immune response in the body.
Others are responsible for protecting cells from oxidative stress.
In addition to brain health, omega 3 also helps with heart health, energy production, supporting hormone synthesis, and regulating inflammation.
How Omega 3 May Help with Dementia Prevention

Now that you have some background information on what omega 3 is and its importance in the body, let’s look at some of the reasons omega 3 and dementia prevention correlate.
To start off, research indicates that oxidative stress and immune response are some of the key contributors to dementia development.
The fact that omega 3 protects against these goes to show that it may have a hand in the prevention of dementia.
Several studies have already been conducted to investigate these claims. These have taken different directions.
Some studies looked into what people with and without the disease eat and how often to see if this has an effect on the disease.
Others involved clinical trials where a percentage of participants were given omega 3 supplements and the rest placebo to compare dementia risk.
The studies focusing on risk of dementia and the consumption of fish produced varying results.
One of the studies supported the notion. It has 2233 participants all older individuals. They were followed for about six years.
The researchers concluded that those participants that were eating fish two times a week has reduced dementia risk by 41% compared to the elderly who were eating it once a month.

Another study had conflicting results where the experts found that there was no difference in dementia risk based on the amount of fish that a person consumed. This is after studying 5,395 individuals for ten years.
While discussing omega 3 and dementia, stakeholders also talk about the anti-inflammatory properties that omega 3 has. These might help with the risk of dementia development.
Raise DHA levels
Persons with dementia usually have low DHA levels in the brain when compared to individuals who do not have the disease.
Many omega 3 supplements contain DHA and EPA according to information on the packaging.
These are essential for human health because they are the main types of omega 3 that exert the most benefit.
DHA helps with cell membrane structural role while EPA assists with body functions like inflammation.
There are also claims that omega 3 fatty acids help to reduce levels of beta-amyloid. These are a marker for dementia in the brain.
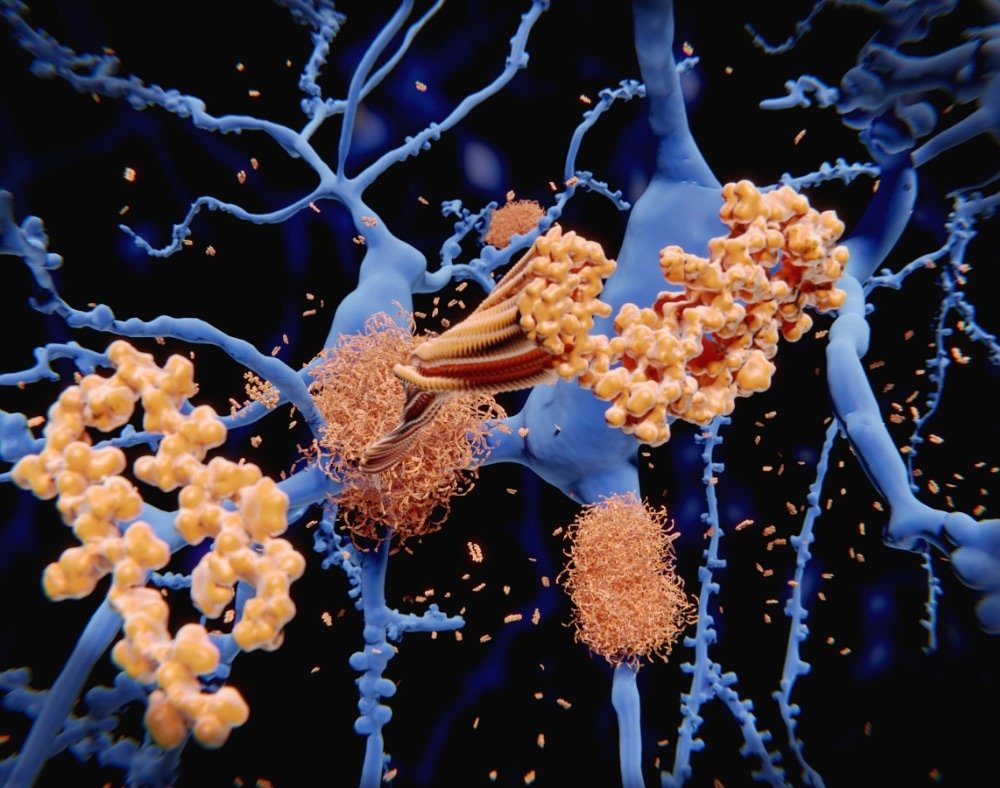
One study published in the journal Neurology researchers stated that people who ate the highest omega 3 levels had the lowest levels of beta-amyloid buildup in the blood.
Clinical trials, on the other hand, although small, have also tried to show the relationship between omega 3 and dementia.
For instance, one study offered 171 people with dementia omega 3 supplements.
It found that there was no cognitive improvement after two years compared to weak persons who were not on the supplements.
Another clinical study studied 437 healthy people who were begging to show some dementia symptoms like troubles with memory recall.
They reported that after taking the omega 3 supplements for 24 weeks there were improvements in learning and recall.
This suggests that omega 3 may improve symptoms during the onset of dementia. On the other hand, it has no effect during the later stages.
Closing Thoughts
To date, the topic on omega 3 and dementia prevention remains highly controversial. Indeed, omega 3 may be good for brain health.
However, there is no overwhelming evidence that it may help prevent dementia development.
Further research is still necessary on this topic. Only that, it will be clearer, whether or not omega 3 is instrumental in the prevention of dementia development.

