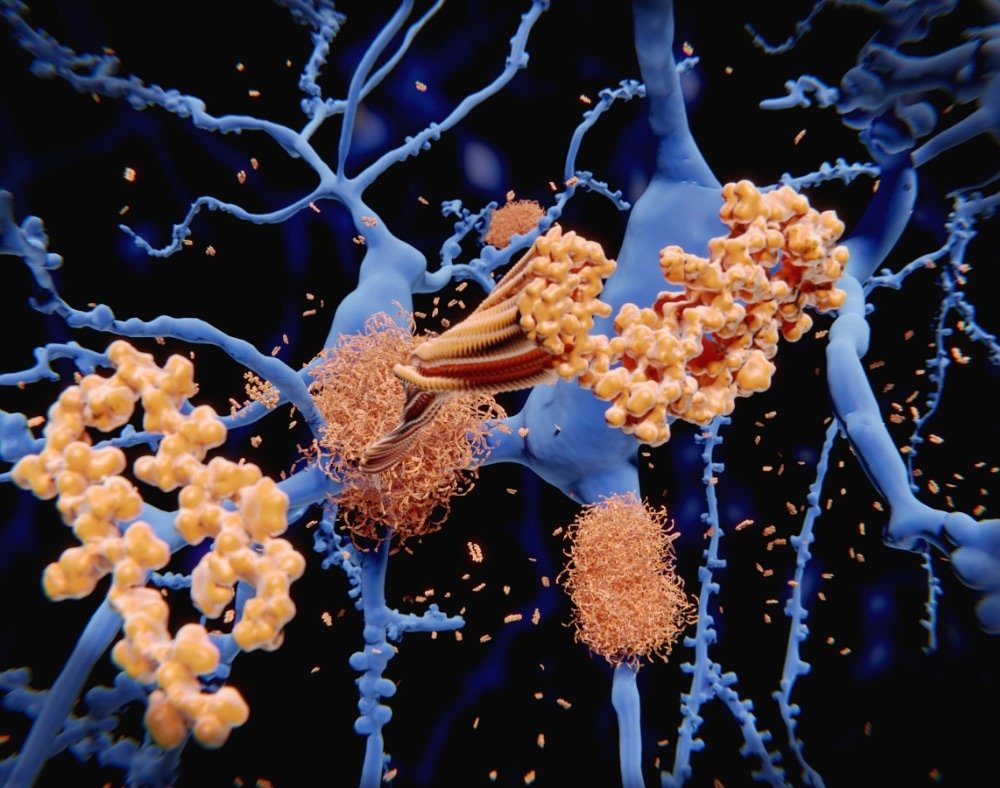
Researchers have conducted several studies to find out if there is a link between the use of sauna and dementia risk.
One study reported that frequent use of the sauna could help to reduce the risk of developing dementia.
This was conducted by researchers from UEF (University of Eastern Finland). They filed their findings in the journal Age and Ageing in 2016.
Does Sauna Protect Against Dementia?
The study assessed the weekly sauna bathing habits of the participants. After this, the experts divided the study participants into three groups”
1. Those who spent about 15 minutes in the sauna 4-7 times in a week (200)
2. Participants who used the sauna 2-3 times a week (1513)
3. Those who only used the sauna once a week (601)
Basis of the Study

The participants of the study included 2,315 healthy men aged between 42-60 years. The study went on for more than two decades.
During the study period, the researchers diagnosed 123 cases of Alzheimer’s disease and 204 dementia cases. The sauna use research analyzed different types of data from the participants, such as:
- Age
- Body mass index
- Smoking status
- Systolic blood pressure
- Alcohol consumption
- Resting heart rate
- Type 2 diabetes
- Previous myocardial infarction
- Serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
The participants in the study used traditional Finnish saunas.
These are the versions that have dry air and recommended temperatures of about 80-100 degrees Celsius. The saunas also increase humidity temporarily by throwing water on the rocks installed inside the sauna heater.
Findings

The researchers stated that there was a link between the use of sauna and dementia risk. They concluded that using the sauna frequently helps to lower the risk of dementia.
The report indicated that the group that was using the sauna about 4-7 times in a week had a 66% lower chance of developing any dementia type.
Additionally, the risk of Alzheimer’s disease was 65 % lower in comparison to the group that was only using the sauna once a week.
Previously, there was a study from KIHD that reported that Finnish men who used 175 degrees dry heat sauna for 4-7 days a week had significantly low death rates resulting from cardiovascular diseases.
According to Jari Laukkanen, the professor who led this sauna research, frequent exposure to heat during sauna bathing not only protects memory, but it also protects the heart.
This is through similar mechanisms that experts do not clearly understand.
He continued to state that it is known that cardiovascular health also has effects on the brain in a statement the professor made to UEF.
The sense of relaxation and well-being that a person experiences during sauna might also play a crucial role.

The researchers, while conducting the study, also note that previous research also suggested that oxidative stress and inflammation were some of the factors that contributed to dementia development.
They explained that their findings were “biologically plausible” because using the saunas regularly reduces inflammation by enhancing vascular endothelial function.
The endothelium is the thin membrane lining found in the blood vessels.
Furthermore, the researchers also explained that their study addresses the use of sauna and dementia reduced risk because bathing in a sauna helps in lowering systemic blood pressure as well as elevated pulse pressure.
These two are well-known dementia risk factors.
Professor Laukkanen also added that while he thought the results of the study were generalizable to other populations in the northern part of the world like North America and Europe, he did not think the same in warmer countries.
Can Everyone Use Saunas?

Because there might be a beneficial link between the use of sauna and dementia risk, you may be wondering whether everyone can use a sauna facility.
While the saunas may be great for a wide range of conditions, they are not appropriate for everyone.
It is necessary that you consult your doctor before starting sauna bathing. This is especially important if you are pregnant or have an underlying medical condition.
Closing Remarks
The benefits people get from using the sauna might be a game-changer in the way the world views dementia.
Experts agree that while sauna use does not substitute exercise, it is a great way to complement a person’s workout routine.
The latest evidence supports the link between the use of sauna and dementia lowered risk because the exercise helps to enhance cardiovascular health reducing the risks of stroke and heart disease.
It also benefits blood vessels, factors that contribute to brain health, which can starve the development of dementia.
More research, however, still needs to be done to determine whether using saunas should be included in the recommendable interventions for preventing different forms of dementia.
Seeing that the study only focused on men, perhaps there also needs one on women to make the studies more inclusive and conclusive.