After weeks of research and study reviews, we bring you this in-depth overview of blood tests for dementia.
Researchers have revealed that conducting a blood test is fast BECOMING A REALITY in dementia diagnosis.
This comes as great news because for the longest time, conducting an autopsy was the only way to get a definitive diagnosis for Alzheimer’s.
Thanks to research and innovation, medics are able to use behavioral tests as well as spinal fluid and brain imaging tests to spot the disease in people before they even start showcasing the initial symptoms of the progressive illness.
These tests, however, are not considered “ideal.” They are not only invasive but are COSTLY and LIMITED to research settings.
They are not part of the care routine for millions of people who are living with this neurodegenerative disorder.
Some tests are not too helpful because they can fail to detect the illness during its early stages.
Brief Introduction to Blood Test for Dementia

Research by scientists in Australia and Japan indicates that a simple blood test will be all that is needed to detect a person who is at risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
It will be possible to get a diagnosis for Alzheimer’s in a doctor’s office without having to go through expensive and invasive procedures.
Doctors will use blood samples to detect the early signs of the illness. A blood test HAS ALREADY BEEN DEVELOPED by C2N Diagnostics in St. Loius, Mo.
This will mainly be used for persons in the US as a routine lab test.
The blood test is regulated under the CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) program from CMS.
For now, the FDA has not yet approved these blood tests. Interested parties can only take the test through a doctor.
If the company wishes, it can sell the rest under commercial laboratories rules. C2N has said that there are plans for the FDA to review this test in 2021.
Alzheimer’s Association stated that it will only endorse this test after the FDA has approved it.
Laboratory tests
The lab test has also received a CE mark implying it can be used as a diagnostic medical device in the European Union. It has met the health, safety, and environmental protection standards for the region.
Michelle Mielke an epidemiologist and neuroscientist at Mayo Clinic expressed her delight in the new development saying that the INNOVATIVE blood-based test for Alzheimer’s is phenomenal.
She explained that the field for very long has been thinking about such an invention. It has finally come to pass.
How the Blood Test for Dementia Works

Also known as the Precitivity AD, the C2N test or blood test for dementia uses mass spectrometry. An analytic technique used to detect specific beta-amyloid protein fragment that is one of the most common hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.
The beta-amyloid proteins normally accumulate and form plaques which can be seen on the brain 2 decades after an individual starts to notice they have memory issues.
The levels of beta-amyloid start to decline in the surrounding fluids as the plaques continue to build up in the brain. These changes can be measured in spinal fluid samples.
It is also possible to measure them in the blood where beta-amyloid concentrations are usually lower.
PrecivityAD is one of the first blood tests for Alzheimer’s that could enable early detection of the neurodegenerative illness.
HOPEFULLY, decades before the first symptoms appear.
Who Can Benefit from Precivity AD and How it Works

Precivity AD is designed for persons between the ages of 60-91. A prescribing physician will ship the blood samples of the person they are treating to be analyzed at C2N’s lab.
The results are normally sent back within ten business days.
A proprietary algorithm is used to calculate the results integrating the age of a person with beta-amyloid measurements and another protein known as apolipoprotein E which influences the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
The results of the blood test are supposed to enhance the accuracy of clinical diagnosis by distinguishing Alzheimer’s dementia from memory loss that is brought about by other medical conditions.
Blood Test Cost Implications
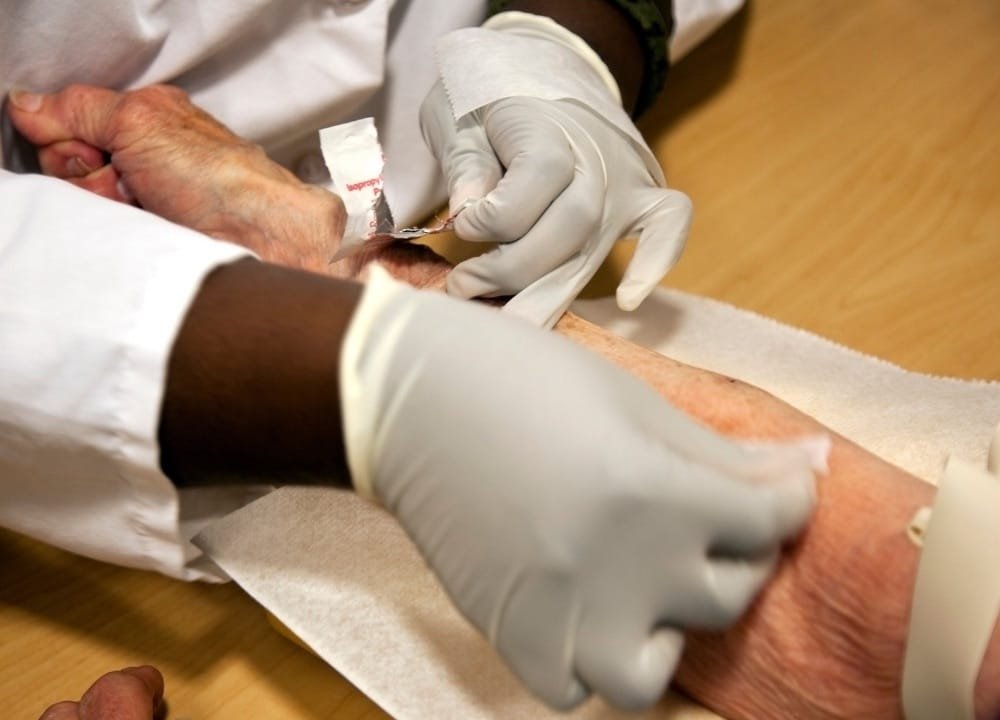
The cost of the test is around $1,250. For now, insurance does not cover this expense.
Thankfully, a person can take advantage of financial assistance programs. And BRING DOWN the expense to around $25-$20 for eligible candidates according to Joel Braunstein chief executive of C2N.
This is more affordable when compared with beta-amyloid tests using PET (positron- emission tomography) brain imaging which normally costs about $5,000 (not covered by insurance).
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) samples typically cost anywhere from $800 to $ 1,000.
Reasons the Blood Test for Dementia is Important

When compared to the difficult and invasive procedures, the blood test for dementia, opens up more exciting possibilities.
Not only for clinical use but therapeutic development explains Adam Boxer a neurologist who works at the University of California, San Francisco.
Blood tests are also very convenient. They can be collected in a person’s home or REMOTE LOCATIONS.
While there is still no medication for Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia, early tests that are readily available can enhance treatment.
They can allow affected persons to take appropriate measures to stay healthy, participate in clinical trials, and plan for their future.
Blood tests are also important because they can help identify the people who are at risk of developing the disease explains Mielke.
The rest can also be used to screen potential participants who can benefit from experimental drugs.
Elisabeth Thijssen a researcher studying blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s at Amsterdam University Medical Centers in the Netherlands said that affordable blood tests can also lower the cost of clinical trials which will give an opportunity for potential treatments to be tested.
This can increase the chance of finally landing a cure.
How Effective is the Blood Test?
C2N reported that they used the Preclivity AD on 168 people. They then compared the results with those of PET scans.
When PET scans showed high amounts of amyloid-beta the blood test agreed 92% of the time.
If there was no amyloid shown after a PET scan, the blood test also gave similar results 77% of the time.
Are there any other Blood Tests for Alzheimer’s?

There is another blood test for dementia that is showing great potential for diagnosing the progressive illness.
Simoa test
It is known as Simoa which stands for “single-molecule array.”
This is also designed to test if there are any proteins in the blood plasma. This test can detect a protein known as ptau181 which has been linked to some of the changes that dementia causes in the brain.
Various studies revealed that Simoa is as effective at predicting dementia development as a spinal tap and PET scans.
The Simoa blood test, however, ELIMINATES the pain, cost, and radioactivity that are associated with the other tests.
Simoa can also detect upcoming changes in the brain that are caused by dementia for both short and long-term i.e. 15 months and 4 years respectively.
At the moment, researchers are using this technology to identify ideal candidates for clinical trials because it is not yet available for many people with the illness.
Apart from Simoa, there are other types of blood tests that are still in development.
Other blood tests
Some are looking into fatty amides or protective fats in the blood.
Studies indicate that if there are increased levels of fatty amide in the blood, it may be an indication of the accumulation of beta-amyloid in the brain.
Researchers are also working on blood tests that will measure other proteins like the NfL (neurofilament light chain) and tau proteins.
Experts claim that brain cell (neuron) death COMMON with individuals with Alzheimer’s may be detected by an increase of the proteins in the blood.
Closing Thoughts
The introduction of the blood test for dementia WILL revolutionize the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
The blood tests will hopefully offer a definitive diagnosis. It will HELP to ELIMINATE the time, pain, and uncertainty of diagnosing the illness.
When the tests become popular, they will have a huge impact on how doctors diagnose dementia.
This may also change the course of treatment. Instead of symptom management, medics may start focusing on the prevention as well as delaying the progression of the disease.
For instance, there may be a possibility that medication can lessen the accumulation of plaques in the brain.