There has been a lot of interest in the topic of lion’s mane and dementia that we received from our users.
Many users are wondering whether lion’s mane offers any health benefits to persons who have dementia.
Can lion’s mane reverse Dementia?
This is based on the fact that the mushroom has been documented to help individuals with several illnesses, including:
-
- Managing diabetes symptoms
- Reducing the risk of heart disease
- Protecting against ulcers in the digestive tract
- Speeding recovery from nervous system injuries
- Fighting against cancer
Before answering whether lion’s mane is beneficial to persons with dementia, it is important to first understand what lion’s mane is.
It is a type of mushroom that is also known as yamabushitake or hou tou gu according to Healthline.
The nootropic food appears to be white, large, and shaggy resembling a lion’s scruff.
The edible fungus is mostly in use in Asian countries like Korea, China, Japan, and India. Mainly for its medical and culinary uses.
You can eat lion’s mane mushrooms raw, cooked, steeped as tea, or dried.
Also, you can get extracts of the mushroom over the counter as health supplements.
Experts reveal that lion’s mane mushrooms have bioactive substances that are beneficial to the human body particularly the gut, heart, and brain.
We uncover how lion’s mane can benefit persons with dementia below.
Note: Feel free to check our top herbs for dementia if you seek more natural ways to alleviate the condition.
Health Benefits of Lion’s Mane

Research focusing on this edible fungus has revealed that it offers multiple health perks.
A study in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry lists numerous benefits of the mushroom saying that it has properties like:
- Anticarcinogenic
- Antibiotic
- Antihypertensive
- Anti-fatigue
- Antidiabetic
- Anti-aging
- Anti-hyperlipodemic
- Hepatoprotective
- Cardioprotective
- Neuroprotective
- Nephroprotective
The study also states that the mushroom enhances cognitive function, depression, and anxiety.
These are common symptoms that persons with dementia have. Very likely the cause that pushed the study of lion’s mane and dementia.
Best Lion’s Mane Products Available on Amazon
Ways Lion’s Mane May Help Individuals with Dementia
People with dementia might benefit from lion’s mane in several ways like:
Boosts Brain Function
Research on this mushroom indicates that it may have a significant impact on neurodegenerative diseases like dementia.
One of the ways lion’s mane affects the function of the brain is through enhancing neurite outgrowth according to research published in the International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms.
This outgrowth can potentially reverse or slow down cell degeneration in the brain which is a character of illnesses like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s (different types of dementia).
The mushroom can help improve memory
Animal research published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine revealed that the mushroom helped to improve memory in mice that had Alzheimer’s and those that did not have.
It also stimulated cognitive function.
A medical trial conducted in Japan affirmed that the edible mushroom helps to improve cognitive function in women and men aged 50-80 years.
Participants of the study took a lion’s mane tablet 3 times a day for 16 weeks. Researchers then continued to observe them for 4 more weeks.
The experts observed that the persons who took lion’s mane scored higher on the cognitive function scale than the group that was on the placebos.
The authors of the study were confident that the mushroom offers an effective treatment for mild cognitive impairment.
Enhance Digestive Health
Lion’s mane is known for its strong anti-inflammatory properties and it may improve the function of the stomach and the digestive system.
Molecules in the mushroom also help to relieve and prevent oxidative stress that is caused by exposure to chemicals in the environment and poor nutrition.
Improve Mental Health and Well-Being- Lion’s mane supplements might help people feel better by reducing mental health effects and improving sleep.
Consuming the mushroom may also be a natural way of treating anxiety and depression.
Furthermore, studies also indicate that the mushroom can enhance immune function.
May Help Protect Against Dementia
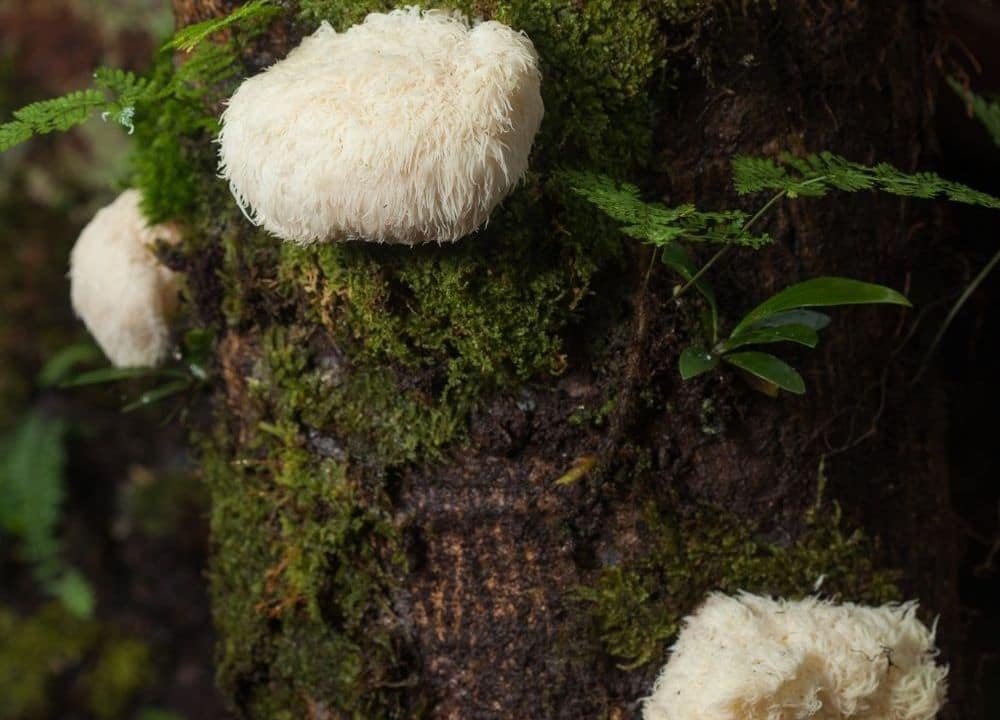

Studies reveal that the lion’s mane mushroom has two special compounds, erinacines and hericeones. These stimulate the growth of brain cells.
Animal studies also report that the mushrooms may help protect against the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
To further talk about lion’s mane and dementia, it’s essential to note that the mushroom and its extracts have been shown to reduce memory loss symptoms in mice.
Researchers also state that it helps to prevent neural damage due to amyloid-beta plaques that accumulate in the brain during AD.
Closing Remarks – Lion’s Mane and Dementia
 Many studies on the subject of lion’s mane and dementia still try to figure out if the mushroom is beneficial for people living with the progressive illness.
Many studies on the subject of lion’s mane and dementia still try to figure out if the mushroom is beneficial for people living with the progressive illness.
This means more research still needs to be done to offer more conclusive results on the protective benefits of the mushroom on the brain.
Always talk to your doctor first before starting taking any supplements.